Getting Started | Building an Application with Angular
Angular 10 Front-end
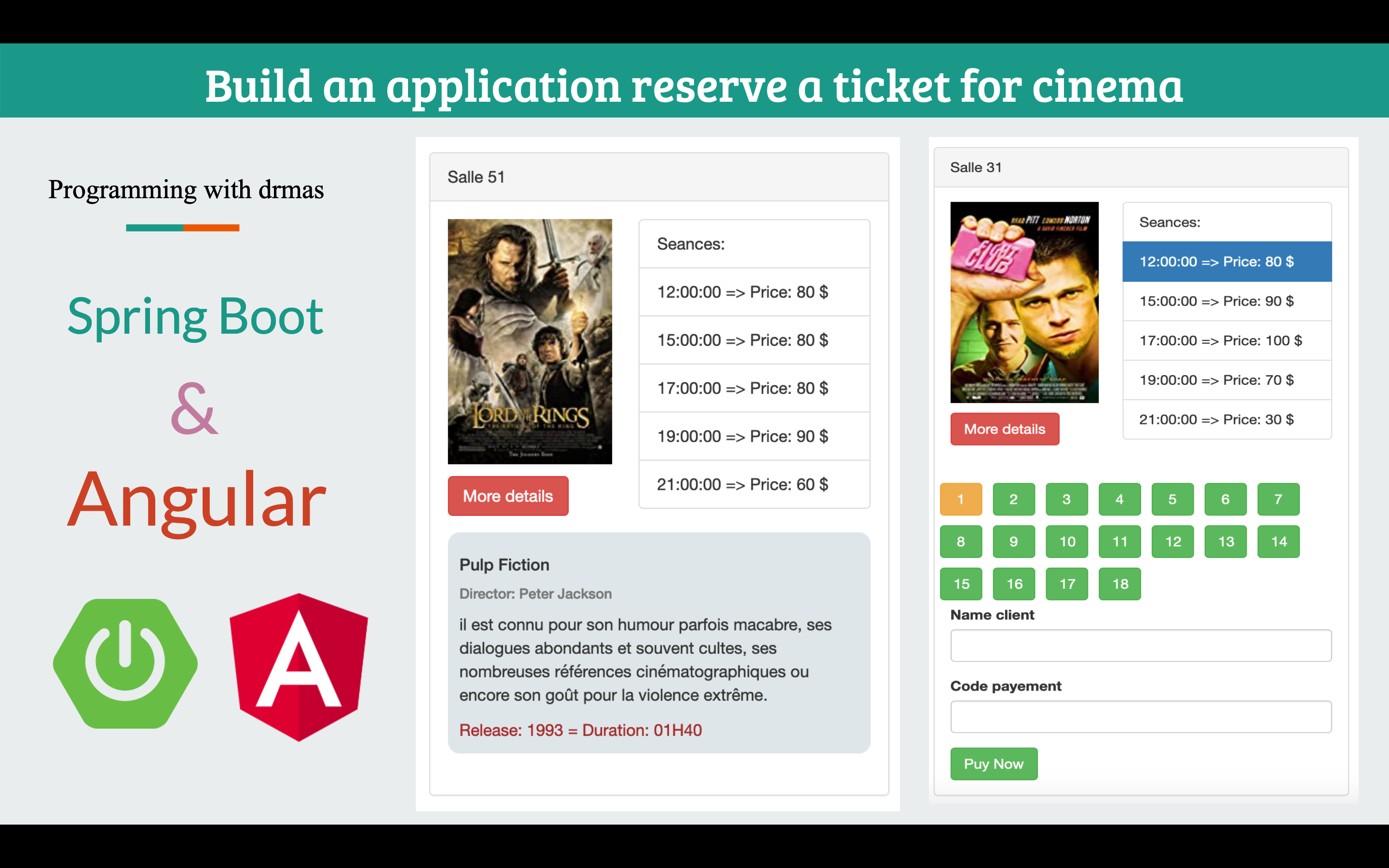
In this tutorial We are going build an application Movies to display the movies we will use the query find by title, find by year, find by director and find by actor. we use mongodb database to develope this project. Front-end side is made with Angular 10, HTTPClient & Router.
Angular CLI version (10.1.1)
ng new
The Angular CLI makes it easy to create an application that already works, right out of the box. It already follows our best practices!
ng generate
Generate components, routes, services and pipes with a simple command. The CLI will also create simple test shells for all of these.
ng serve
Easily test your app locally while developing.
$ npm install -g @angular/cli
$ ng new cinema
$ cd cinema
$ ng serve
Technology
Angular 10
Angular HTTPClient
Angular Router
Project Structure
Install Bootstrap CSS framework
Bootstrap a framework to encourage consistency across internal tools. Before Bootstrap, various libraries were used for interface development, which led to inconsistencies and a high maintenance burden. According to Twitter developer Mark Otto:
Use the following command to install bootstrap in the project.
$ npm install bootstrap --save
Angular Services
Angular services are singleton objects that get instantiated only once during the lifetime of an application. They contain methods that maintain data throughout the life of an application, i.e. data does not get refreshed and is available all the time. The main objective of a service is to organize and share business logic, models, or data and functions with different components of an Angular application.
An example of when to use services would be to transfer data from one controller to another custom service.
Why Should We Use Services in Angular? The separation of concerns is the main reason why Angular services came into existence. An Angular service is a stateless object and provides some very useful functions. These functions can be invoked from any component of Angular, like Controllers, Directives, etc. This helps in dividing the web application into small, different logical units which can be reused.
Create three services in the service package
- CinemaService
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class CinemaService {
private host = 'http://localhost:8080/api';
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
getCities() {
return this.http.get(this.host + '/cities');
}
getCinemas(city) {
return this.http.get(city._links.cinemas.href);
}
getSalles(cinema) {
return this.http.get(cinema._links.salles.href);
}
getProjections(salle) {
const url = salle._links.projections.href.replace('{?projection}', '');
return this.http.get(url + '?projection=p1');
}
getTicketPlaces(proj) {
const url = proj._links.tickets.href.replace('{?projection}', '');
return this.http.get(url + '?projection=ticketsProj');
}
puyTickets(dataForm) {
return this.http.post(this.host + '/puyTickets', dataForm);
}
findFilmById(id) {
return this.http.get(this.host + `/findFilmById/${id}`);
}
}
Create cinema page
Now we'll continue with the project by adding pages which are the basic buildings of an Ionic app. So let's get started. You can create pages either manually or generating them using the Ionic CLI v5 which is the recommended method. In this guide we'll look first at how to create a page generate it with the Ionic CLI, then how to add it to the project.
- cinemaWe are going to create a cinema page to display all cities, cinemas, movies and tickets information.
src/app/cinema-component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute} from '@angular/router';
import { CinemaService } from '../service/CinemaService';
@Component({
selector: 'app-cinema',
templateUrl: './cinema.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./cinema.component.css']
})
export class CinemaComponent implements OnInit {
selectedTickets: any[] = [];
public: cities;
public: cinemas;
public: salles;
public: currentCity;
public: currentCinema;
public: currentProjection;
public: cityName;
public: film;
public = showDetails = false;
constructor(public cinemaService: CinemaService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.cinemaService.getCities().subscribe(cities => {
this.cities = cities;
});
}
moreDetails(id) {
this.cinemaService.findFilmById(id).subscribe(film => {
this.film = film;
this.showDetails = !this.showDetails;
})
}
onGetCinema(city) {
this.currentCity = city;
this.salles = undefined;
this.cityName = city.name;
this.cinemaService.getCinemas(city).subscribe(cinemas => {
this.cinemas = cinemas;
});
}
onGetSalle(c) {
this.currentCinema = c;
this.cinemaService.getSalles(c).subscribe(data => {
this.salles = data;
this.salles._embedded.salles.forEach(salle => {
this.cinemaService.getProjections(salle).subscribe(salles => {
salle.projections = salles;
});
});
});
}
onGetPlaces(p) {
this.currentProjection = p;
this.cinemaService.getTicketPlaces(p).subscribe(data => {
this.currentProjection.tickets = data;
this.selectedTickets = [];
});
}
onSelectTicket(t) {
if (!t.selected) {
t.selected = true;
this.selectedTickets.push(t);
} else {
t.selected = false;
this.selectedTickets.splice(this.selectedTickets.indexOf(t), 1);
}
}
getTicketClass(t) {
let str = 'btn ';
if (t.reserve === true) {
str += 'btn-danger';
} else if (t.selected) {
str += 'btn-warning';
} else {
str += 'btn-success';
}
return str;
}
onPayTicket(dataForm) {
const tickets = [];
this.selectedTickets.forEach(t => {
tickets.push(t.id);
});
dataForm.tickets = tickets;
this.cinemaService.puyTickets(dataForm).subscribe(data => {
dataForm = data;
alert('Tickets Réservés avec success !');
this.onGetPlaces(this.currentProjection);
});
}
}
src/app/cinema-component.html
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3">
<ul *ngIf="cities" class="list-group">
<li class="list-group-item list-group-item-danger">Find Cinemas By City</li>
<li [ngClass]="city==currentCity?'active':''" *ngFor="let city of cities._embedded.cities" class="list-group-item clickable"
(click)="onGetCinema(city)">{{city.name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="col-md-9">
<div class="panel panel-danger">
<div class="panel-heading">Cinema For {{cityName}} </div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul *ngIf="cinemas" class="nav nav-pills">
<li [ngClass]="cinema==currentCinema?'active':''" *ngFor="let cinema of cinemas._embedded.cinemas" class="clickable">
<a (click)="onGetSalle(cinema)" style="color: darkred"> {{cinema.name}} </a>
</li>
</ul>
<br>
<div class="row" *ngIf="salles">
<div *ngFor="let salle of salles._embedded.salles" class="col-sm-6">
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="panel-heading">{{salle.name}}</div>
<div class="panel-body" *ngIf="salle.projections">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-5">
<img src="{{salle.projections._embedded.projections[0].film.photo}}" alt="{{salle.projections._embedded.projections[0].film.photo}}">
<button class="btn btn-danger" style="margin-top: 10px;" (click)="moreDetails(salle.projections._embedded.projections[0].film.id)">More details</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-7">
<ul class="list-group">
<li class="list-group-item">Seances:</li>
<li [ngClass]="proj==currentProjection?'active':''"
(click)="onGetPlaces(proj)" *ngFor="let proj of salle.projections._embedded.projections" class="list-group-item clickable">
{{proj.seance.startTime}} => Price: {{proj.price|number:'0.00'}} $
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<div class="card" *ngIf="showDetails && salle.projections._embedded.projections[0].film.id==film.id">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{film.title}}</h5>
<h6 class="card-subtitle mb-2 text-muted">Director: {{film.director}}</h6>
<p class="card-text">{{film.description}}</p>
<a href="#" class="card-link">Release: {{film.releaseDate}} = </a>
<a href="#" class="card-link">Duration: {{film.duration}}</a>
</div>
</div> <br>
<div *ngIf="currentProjection">
<div *ngIf="salle.id==currentProjection.salle.id">
<div class="row" *ngIf="currentProjection.tickets">
<button class="{{getTicketClass(t)}} ticket" (click)="onSelectTicket(t)" [disabled]="t.reserve==true"
*ngFor="let t of currentProjection.tickets._embedded.tickets">
{{t.place.number}}
</button>
</div>
<div *ngIf="selectedTickets.length>0">
<form #f="ngForm" (ngSubmit)="onPayTicket(f.value)">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label">Name client</label>
<input class="form-control" name="nameClient" ngModel type="text"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label">Code payement</label>
<input class="form-control" name="codePayment" ngModel type="text"/>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-success" type="submit">Puy Now</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
src/app/cinema-component.css
.clickable{
cursor: pointer;
}
.ticket {
margin: 5px;
width: 40px;
text-align: center;
}
.card {
background: #dfe6e9;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
}
.card a {
color: brown;
}
src/app/app.component.html
<div class="topnav">
<a class="active" routerLink="/cinema">Home</a>
<a routerLink="/cinema">News</a>
<a routerLink="/cinema">Contact</a>
<a routerLink="/cinema">About</a>
<a routerLink="/cinema">Cinema</a>
</div><br><br>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
src/app/app.component.css
body {
margin: 0;
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.topnav {
overflow: hidden;
background-color: #333;
}
.topnav a {
float: left;
color: #f2f2f2;
text-align: center;
padding: 14px 16px;
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 17px;
}
.topnav a:hover {
background-color: #ddd;
color: black;
}
.topnav a.active {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
}
Add the AppRoutingModule
In Angular, the best practice is to load and configure the router in a separate, top-level module that is dedicated to routing and imported by the root AppModule.
By convention, the module class name is AppRoutingModule and it belongs in the app-routing.module.ts in the src/app folder.
app-routing-module.ts
src/app/app-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { CinemaComponent } from './cinema/cinema.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
redirectTo: 'cinema',
pathMatch: 'full'
},
{
path: 'menu',
component: CinemaComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(routes)
],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
NgModules and JavaScript modules
The NgModule system is different from and unrelated to the JavaScript (ES2015) module system for managing collections of JavaScript objects. These are complementary module systems that you can use together to write your apps.
In JavaScript each file is a module and all objects defined in the file belong to that module. The module declares some objects to be public by marking them with the export key word. Other JavaScript modules use import statements to access public objects from other modules.
app-module.ts
src/app/app-module.ts
import { AddPaymentComponent } from './payments/add-apyment/add-payment.component';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule, CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA, NO_ERRORS_SCHEMA } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { MaterialModule } from './material-module';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component';
import { AdminDashboardComponent } from './admin-dashboard/admin-dashboard.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
CinemaComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
HttpClientModule,
MaterialModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule,
AppRoutingModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
schemas: [ CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA, NO_ERRORS_SCHEMA ]
})
export class AppModule { }
Conclusion
Now we have an overview of Angular 10 + Spring Boot App.
We also take a look at client-server architecture for REST API using Spring Web MVC & Spring Data JPA, as well as Angular 10 project structure for building a front-end app to make HTTP requests and consume responses.